Gluten, a common protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, may seem harmless. However, for some, it can quietly cause significant health problems. Without clear warning signs, gluten sensitivity can go undetected, potentially leading to long-term damage. Recognizing the signs of gluten sensitivity is key to maintaining good health.
1. Gastrointestinal Distress
Digestive issues like nausea, bloating, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and constipation are hallmark symptoms of gluten sensitivity. Often misdiagnosed as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)—a condition affecting 10-15% of the global population—these symptoms can persist without proper treatment. If your digestive issues worsen after consuming gluten, it could be the underlying cause.
2. Unexplained Weight Changes
Unexpected weight gain or loss without a clear reason can be linked to gluten intolerance. These fluctuations are often due to inflammation and metabolic disruption caused by gluten. If unexplained weight changes coincide with other signs of malabsorption, gluten sensitivity may be the culprit.
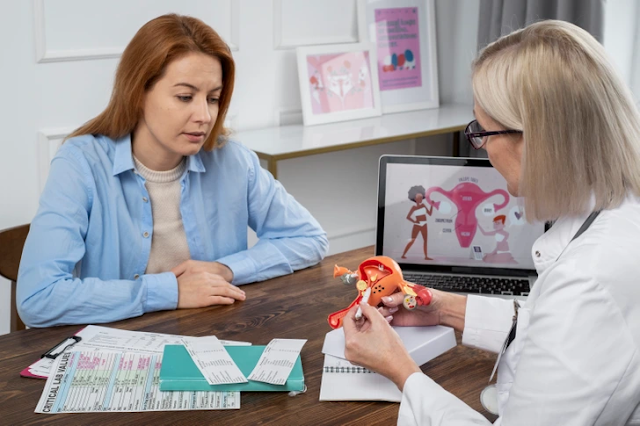
3. Hormonal Imbalances
 |
| © freepik / Freepik |
Gluten intolerance can disrupt hormone regulation, leading to irregular menstrual cycles, PMS, sleep disturbances, and unexplained weight changes. Women may notice these symptoms intensify during life stages like puberty, pregnancy, or menopause.
4. Neurological and Psychological Symptoms
 |
| © julos / Freepik |
Gluten can increase inflammation and intestinal permeability, triggering symptoms such as brain fog, depression, anxiety, insomnia, and fatigue. Many individuals with gluten sensitivity also experience migraines, often occurring 30-60 minutes after eating gluten-containing foods.
5. Skin and Nail Conditions
Gluten sensitivity may manifest in the skin as keratosis pilaris or herpetiform dermatitis, characterized by itchy, red rashes that can appear on the face, hands, elbows, and other areas. It can also cause brittle nails and skin irritations similar to eczema.
6. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
 |
| © Depositphotos.com |
ADHD, which affects both children and adults, may have a connection to gluten intolerance. Symptoms such as poor attention span and difficulty concentrating might improve on a gluten-free diet, according to emerging research.
7. Dental Problems
 |
| © Depositphotos.com, © Depositphotos.com |
Gluten intolerance can impair nutrient absorption, leading to deficiencies in calcium and other essential minerals. This may result in dental issues like tooth decay, enamel sensitivity, cavities, and recurring mouth ulcers despite good oral hygiene.
8. Iron Deficiency Anemia
 |
| © krakenimages.com / Freepik |
Iron deficiency anemia is often a key indicator of celiac disease. Symptoms include fatigue, pale skin, shortness of breath, and headaches. Gluten sensitivity hinders the intestine’s ability to absorb iron, which can lead to persistent anemia despite dietary iron intake.
9. Autoimmune Disorders
Individuals with gluten intolerance may be at higher risk for autoimmune diseases. Conditions like autoimmune thyroiditis, diabetes, Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis are often linked to celiac disease, an autoimmune reaction to gluten.
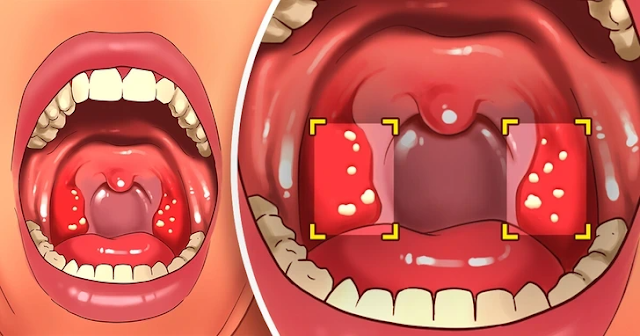
10. Tonsil Stones
While not widely studied, many gluten-sensitive individuals report experiencing tonsil stones that resolve after adopting a gluten-free diet. This suggests a potential connection between the two.
Managing Gluten Sensitivity
 |
| © pixabay.com |
If you suspect gluten sensitivity, follow these steps:
- Get Tested: Consult your doctor for a blood test to check for antibodies associated with celiac disease. Ensure you’re consuming gluten before the test for accurate results.
- Eliminate Gluten: Avoid foods containing wheat, rye, bulgur, semolina, and other gluten sources. Opt for gluten-free products and carefully read food labels.
By identifying and managing gluten sensitivity early, you can protect your health and improve your quality of life.





Post a Comment